Can Augmented Reality Lessen Downtime?
Rockwell Automation created a short YouTube video about how augmented reality tools can help reduce downtime of machines and productivity. While the video is geared toward specific products, the company also released an extensive video webinar that was published via Auto.com delving deeper into the use of augmented reality to save time—especially machine downtime.
Can augmented reality lessen downtime at work? The short answer is yes. Rockwell Automation gives four reasons in its video on how augmented reality is effective:
- “AR doesn’t disrupt existing technology. AR exists in parallel to OT and IT technology, without disrupting existing infrastructure and investments.”
- “AR requires a low technical hurdle. With the right tools, subject matter experts can create and refine effective AR content with little to no coding experience.”
- “AR can utilize existing digital assets. Repurposed CAD and other digital files created during the design of physical equipment can enrich AR experiences.”
- “AR is flexible and extensible. AR experiences can easily be updated to reflect changes to products and procedures. AR is less dependent on translation requirements.”
If all this sounds quite like a technological explanation, that’s because it sort of is a technological explanation. The video from Rockwell Automation that was posted to Auto.com is a bit extensive—running for more than 40 minutes. However, it delves into the heart of why augmented reality might be a crucial adaptation for factories and businesses.
Downtime is Costly!
No video has to explicitly state that downtime is costly. Minutes lost to someone waiting for an answer on how to handle a problem, fix a machine or manage a task can waste billable business hours. Of course, if production is affected, that downtime also could hurt profits. So costly are these incidents that Garvey Conveyers hilariously—and perhaps truthfully—refers to the word downtime as a four letter word.
In 2013, Industry Week and Stratus Technologies teamed up for the second Manufacturer IT Applications Study. Frank Hill, with Stratus, revealed the study results to Industry Week. Hill noted that the cost of a downtime incident clocks in at about $17,000, and there might be about seven incidents each year.
One of the problems that Hill noted from the results is that while many manufacturers have “traditional backup” for their systems, this isn’t a time efficient solution. Restoring data could take days. Hill explained that companies “…need to make the right technology investments to keep their critical applications up and running.” The solution pointed to technology that was “always on.”

How is Augmented Reality Beneficial?
Hill didn’t specifically mention augmented reality from the study results, but Augmenta explains that augmented reality can help prevent downtime incidents and maximize time efficiency in repairs.
Augmented reality technology can prevent incidents by notifying workers of issues before they may become a problem. Think about augmented reality in vehicles. The predictive technology can help pinpoint obstacles on the road and warn drivers about other issues. Machines aren’t so different. Perhaps augmented reality technology could alert an employee that a belt is in need of repair. As Augmenta noted, augmented reality can help employees stop a problem before it becomes a major issue.
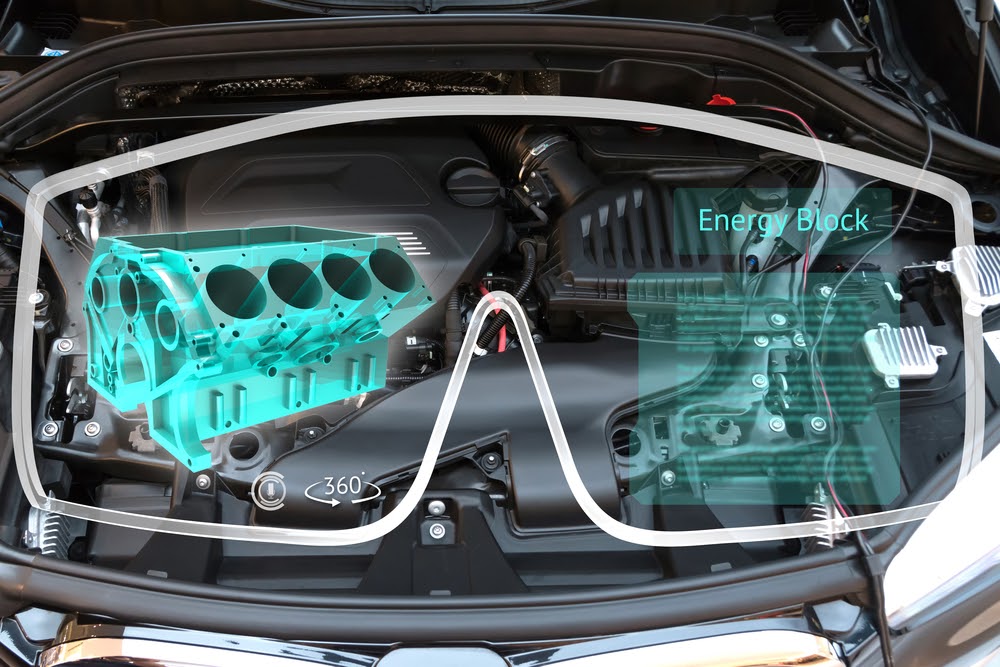
Repairs also can be aided with the help of augmented reality. Many automobile manufacturers use augmented reality glasses to aid technicians in repair. These glasses show problems and solutions in front of the technician’s eyes. There is no need to stop in the middle of repairs and check a reference guide. Some of these glasses even allow the technician to connect to additional support personnel—hands-free!
In the manufacturing environment, augmented reality can keep techs focused on their tasks and save them time during repairs. Perhaps the technology even lets them connect to a help desk, too. In the past, fixing a machine could have required contacting numerous people by phone or consulting a manual. Now technology can simplify the process and save time.
The Adaptability of Augmented Reality
For manufacturers and other businesses, augmented reality also could be an adaptable technology. Companies can use existing files for an augmented reality experience, according to Rockwell. For example, the augmented reality program could include data files or information related to repairs or other details.
These programs, as Rockwell also noted, can be changed and updated as needed. If something changes, the augmented reality experience can be updated to reflect the new information.
Manufacturing Business Technology cites Lockheed Martin’s success with augmented reality. The company builds spaceships, so there is no room for any error. When Lockheed Martin implemented augmented reality for the Space division, the company saw “…a 35-50 percent reduction in overall technician time, a 90-99 percent reduction in the time it takes technicians to interpret drawings and text instructions and an 85 percent reduction in overall time for training.”
Augmented reality allowed techs to see instructions and details overlaid on actual aircraft. The visual guidance provided likely meant that the techs didn’t have to reread text or consult with another technician.
Augmented Reality Aiding Automotive
In the automotive sector, augmented reality and virtual reality is used to simplify processes and aid in collaboration. Augmented reality also is being used to aid repairs in the industry.
Motortrend reported in September that Mercedes Benz technicians are eyeing repairs with HoloLens 2 glasses. The goggles let techs show issues to other experts virtually. The expert can make notes about repairs—they can actually visually note issues on the car to point out the problem. Both the tech and the expert see the engine, and the technology will superimpose arrows or other notes to show issues.
The technology doesn’t come cheap to dealers, however. Motortrend reported that the price of the augmented reality experience is $10,000 per dealer.
Manufacturers also are using virtual reality as a means of collaborating remotely. Ford used virtual reality during the pandemic to allow executives to discuss design details. With virtual reality, executives could use laser pointers to note any details on the car (which was also a virtual model). Executives also could switch positions with each other to gain a different vantage point.
Augmented Reality and the Consumer
While augmented reality benefits companies and manufacturers by decreasing downtime and aiding in repairs, the technology also has many benefits to consumers. Augmented reality follows consumers each day they drive.
Many new car models feature augmented reality within heads-up displays. The most basic form of augmented reality is the rear back-up cameras. The cameras show the real world view behind the car, but the technology also projects grid lines to show drivers their turning radius. Those superimposed gridlines are a hallmark of augmented reality.
More advanced heads-up displays, however, are being introduced constantly in new car models. Mercedes Benz introduced the new MBUX Hyperscreen (MBUX stands for Mercedes Benz User Experience). The Hyperscreen is massive at 56 inches and includes voice recognition and augmented reality features.
Augmented reality in the car might become even more detailed. While many cars include front and rear cameras or even heads-up displays that feature augmented reality elements (like arrows for navigation), Nissan is working on the ultimate in-car technology. Invisible-to-Visible (I2V) would feature avatars of friends or family to make the ride more enjoyable. However, drivers also could have a professional driver join them (as an avatar) for advice. I2V also would allow for the windows to project bright skies to create a joyful ambiance. Road obstacles and other hazards could be predicted with I2V, and the driver would be alerted ahead of time.

Augmented Reality and Consumer Downtime
Downtime in industry terms is related to manufacturing, and while augmented reality can lessen downtime for the manufacturing sector, it also could aid consumers, too. Shopping can be simplified with augmented reality and the technology also can heighten the user experience.
Buying cosmetics or clothes can be a guessing game. Sizes vary, and colors don’t look the same on each person. Augmented reality try-on experiences allow consumers to preview their choices before they buy. This can save time for the consumer, but it also could decrease returns for the company.
Even car shopping can be simplified with augmented or virtual reality. Online showrooms exist in virtual and augmented reality to help consumers find their ideal car. With augmented reality, users can drop their car of choice into their real-world environment. Virtual reality showrooms can be accessed online or by wearing a virtual reality headset. Both types of showrooms allow users to swap out paint hues and look inside the vehicles.
Even home improvement can be simplified with augmented reality. Thinking about painting a bedroom a new hue? Preview the color choices with augmented reality! Some companies let users photograph their room and then superimpose new paint colors to try-on the paint! This can help homeowners decide what hue will complement their décor…and what hues to avoid completely!
Downtime is money wasted, both for the consumer and a manufacturer. Augmented reality can have the same time and eliminate downtime. Augmented reality allows technicians to make repairs without pausing to consult a book or an expert. The technology also helps stop accidents before they happen; augmented reality can alert companies that a machine needs a repair or that a part might be failing.
The same benefits apply to consumers, too—especially in the car. Augmented reality features in the car could provide additional safety benefits (like a backup camera), and the technology also helps simplify the drive (through graphic directions). Augmented reality also can help consumers while shopping for new clothes, cosmetics or even deciding on a new paint hue. Visualizing choices or instructive content can provide yet another aid to simplify decisions and processes…and save time!
Recent Posts
Categories
Luxury Cars
Trucks
Sedans